The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data privacy regulation that came into effect in the European Union on May 25, 2018. It aims to protect the personal data of EU citizens and requires businesses to implement appropriate measures for securing this sensitive information.
Toc
- 1. Introduction to PII and Its Importance
- 2. Understanding PII Data Categories
- 3. Best Practices for Protecting PII under GDPR
- 4. Related articles 01:
- 5. Legal and Regulatory Frameworks for PII Protection
- 6. Risks Associated with PII Data Breaches
- 7. Related articles 02:
- 8. Implementing Effective PII Protection Measures
- 9. Tools and Technologies for PII Protection
- 10. Conclusion
This guide will focus on the protection of personally identifiable information (PII) under GDPR and provide best practices for securing PII in compliance with the regulation.
Introduction to PII and Its Importance

In today’s digital landscape, protecting Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is more crucial than ever. PII includes any data that can be used to identify an individual, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and financial details. For website administrators, ensuring the security of this sensitive information is not just a legal obligation but also a critical component of maintaining user trust and safeguarding against cyber threats.
What is Personally Identifiable Information (PII)?
Personally Identifiable Information, or PII, refers to any data that can be used to identify an individual. This includes:
- Name
- Address
- Date of birth
- Social security number
- Email address
- Phone number
- IP address
- Biometric data (e.g. fingerprints, facial recognition)
The Importance of Protecting PII
The rise of technology and the internet has made it easier than ever for personal information to be collected, stored, and shared. As a result, there has been an increase in identity theft and cyber attacks targeting sensitive data.
Under GDPR, businesses are required to protect PII and ensure that it is only processed if there is a lawful basis for doing so. Failure to comply with GDPR can result in significant fines and damage to a company’s reputation. Additionally, protecting PII helps build trust with customers and promotes good data security practices.
Understanding PII Data Categories
PII can be categorized into different types based on the level of sensitivity:
Basic PII
Basic PII refers to information that, on its own, can be used to identify an individual, but may not necessarily provide in-depth insight into their personal life. This category includes data such as names, email addresses, and phone numbers. While this information may seem harmless, it can still be exploited when combined with other data sources, making its protection essential.
Sensitive PII
Sensitive PII includes information that is more revealing and carries a higher risk of harm if disclosed. This category encompasses data such as social security numbers, financial account details, and medical records. Due to the potential consequences associated with a breach of sensitive PII, it is crucial for organizations to enforce stricter security measures and access controls.
Pseudonymous PII
Pseudonymous PII is data that can no longer be attributed to a specific individual without the use of additional information. While pseudonymization can help enhance privacy, it is important to note that this data is still subject to GDPR and must be protected appropriately. Organizations should take steps to ensure that pseudonymous data is not easily re-identified through other means.
In summary, understanding the different categories of PII is fundamental in developing effective data protection strategies that comply with GDPR. Organizations must assess the sensitivity of the data they handle and implement appropriate security measures tailored to the specific risks associated with each category.
Best Practices for Protecting PII under GDPR

Under GDPR, businesses are required to implement appropriate technical and organisational measures for protecting personal data. Here are some best practices to help ensure the security of PII:
Conduct a Data Audit
The first step in securing Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the data your business collects, processes, and stores. Conducting a thorough data audit involves not just cataloging the types of data, but also assessing how it flows through your systems and identifying which departments have access to it. This process can help highlight any potential vulnerabilities or gaps in your security measures, allowing you to take proactive steps to address them.
Implement Strong Access Controls
One of the most effective strategies for protecting sensitive data is to limit access through the implementation of strong access controls. This includes not only the use of complex passwords but also the adoption of multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security. Additionally, role-based permissions should be established to ensure that employees have access only to the data necessary for their job functions, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Encrypt Sensitive Data
Data encryption is a powerful and essential method for safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access. By converting data into a coded format, encryption makes it significantly more difficult for cybercriminals to exploit. Under GDPR regulations, encryption is recognized as an appropriate and effective security measure for protecting PII, helping businesses comply with legal requirements and enhance their overall data security posture.
1. https://instaproapk.mobi/unleashing-the-power-nvidia-b100-for-gamers/
2. https://instaproapk.mobi/unlocking-small-business-potential-with-microsoft-access/
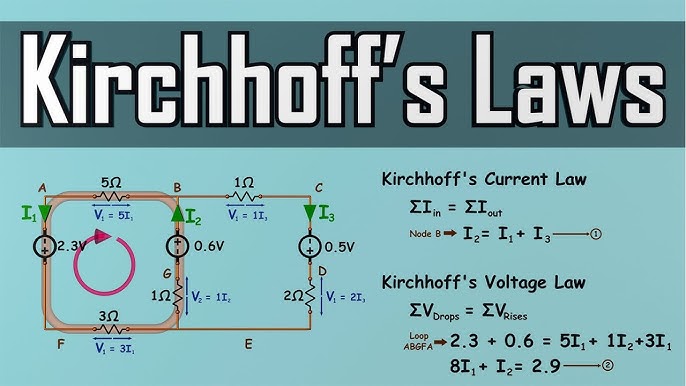
3. https://instaproapk.mobi/demystifying-kirchhoffs-laws-kcl-and-kvl-explained/
4. https://instaproapk.mobi/revolutionizing-hr-microsoft-viva-unveiled/
5. https://instaproapk.mobi/unlocking-creativity-with-adobe-cs6-a-guide-for-professionals/
Train Employees on Data Protection
Employees are often considered the weakest link in the chain of data security, making it vital to prioritize their training. Providing comprehensive training programs that cover the principles of data protection, identifying phishing attempts, and understanding the importance of secure data handling can significantly reduce the risk of human error. Regular reminders, workshops, and updates about best practices should also be part of an ongoing effort to keep data protection top of mind for all staff members.
Have a Data Breach Response Plan in Place
Despite all the precautions taken, data breaches can still occur, making it crucial to have a well-defined response plan in place. This plan should outline the steps to be taken immediately following a breach, including how to contain the situation, assess the damage, and notify affected parties in compliance with GDPR’s notification requirements. Regularly testing and updating this plan ensures that your team is prepared to respond effectively and minimizes the potential impact of a data breach on your organization and its stakeholders.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks for PII Protection

Various laws and regulations mandate the protection of PII, including:
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the EU
GDPR is a comprehensive data privacy regulation that applies to all businesses operating in the European Union (EU). It aims to give individuals control over their personal data and impose strict requirements on organizations handling and processing PII. Non-compliance with GDPR can result in significant fines, making it essential for businesses to comply with its principles and regulations.
CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the US
The CCPA is a landmark piece of legislation that enhances privacy rights and consumer protection for residents of California. It grants individuals the right to know what personal information is being collected about them, the right to access that information, and the right to request its deletion. Businesses must inform consumers about the categories of data collected and the purpose for which it is used. Compliance with CCPA is crucial for organizations operating in California, as non-compliance can result in substantial fines and legal repercussions.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
In the healthcare sector, HIPAA establishes standards for protecting sensitive patient information. It mandates that healthcare providers, insurers, and their business associates implement safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of protected health information (PHI). HIPAA compliance is essential for healthcare organizations, as violations can lead to severe penalties, including fines and loss of licensure.
Other Global Privacy Laws
Apart from GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, various other regulations exist worldwide that focus on PII protection, such as the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) in Canada, the General Data Protection Law (LGPD) in Brazil, and the Data Protection Act in the UK. Understanding the legal landscape of PII protection globally is vital for organizations that operate across borders, as each jurisdiction may have its own specific requirements and implications for compliance.
By being aware of these laws and regulations, organizations can better protect personal data, mitigate risks, and ensure trust and security for their customers. Compliance not only protects individuals’ rights but also safeguards businesses from legal and financial repercussions.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) for payment information security
While not specifically focused on PII protection, PCI DSS is an essential consideration for businesses that handle payment information. It outlines security standards and requirements for organizations that process credit card payments to protect against data breaches and fraud. Compliance with PCI DSS is necessary for any business that accepts credit or debit card payments. Failure to comply can result in significant fines, loss of customer trust, and damage to the company’s reputation.
Read more:
https://instaproapk.mobi/demystifying-kirchhoffs-laws-kcl-and-kvl-explained
https://instaproapk.mobi/unleashing-the-power-nvidia-b100-for-gamers/
https://instaproapk.mobi/unlocking-small-business-potential-with-microsoft-access/
https://instaproapk.mobi/revolutionizing-hr-microsoft-viva-unveiled/
https://instaproapk.mobi/unlocking-creativity-with-adobe-cs6-a-guide-for-professionals/
Risks Associated with PII Data Breaches

The consequences of a PII data breach can be severe, including:
Financial Loss
Financial loss is one of the most immediate and direct consequences of a PII data breach. Organizations may incur substantial costs related to forensic investigations, legal fees, regulatory fines, and customer compensation. Additionally, the financial impact can be compounded by the costs associated with implementing remedial measures and enhancing security postures to prevent future breaches. Moreover, businesses may experience a decline in revenue due to loss of customer trust, as affected customers may choose to take their business elsewhere, leading to long-term financial repercussions.
1. https://instaproapk.mobi/unlocking-creativity-with-adobe-cs6-a-guide-for-professionals/
2. https://instaproapk.mobi/unlocking-small-business-potential-with-microsoft-access/
3. https://instaproapk.mobi/demystifying-kirchhoffs-laws-kcl-and-kvl-explained/
4. https://instaproapk.mobi/revolutionizing-hr-microsoft-viva-unveiled/
5. https://instaproapk.mobi/unleashing-the-power-nvidia-b100-for-gamers/
Reputational Damage
Data breaches can severely damage an organization’s reputation. Customers and partners may perceive a breach as a failure in the company’s ability to protect sensitive information. This erosion of trust can lead to negative publicity, which may take years to recover from. Businesses may struggle to regain their standing in the market, and a tarnished reputation can also deter potential clients or investors, further impeding growth and success.
Legal Repercussions
In the wake of a data breach, organizations may face legal actions from affected individuals or groups whose PII was compromised. Lawsuits can arise from negligence, leading to potential settlements or judgments against the company. Additionally, regulatory bodies may impose fines and other penalties for non-compliance with data protection regulations, which can add to the financial burden and create ongoing legal challenges for the organization.
Operational Disruption
Experiencing a data breach can disrupt business operations as resources are diverted to manage the incident and restore systems. This includes addressing security flaws, conducting audits, and implementing security enhancements, all of which can divert attention from core business activities. The resultant operational inefficiencies can hinder productivity and affect overall performance, compounding the impact of the breach on the organization.
Implementing Effective PII Protection Measures

Perform a Comprehensive Audit
A thorough audit helps identify all points where PII is handled:
- Map data flows within your website and organization.
- Identify data collection forms, databases, and third-party service providers.
- Determine the type and sensitivity of data collected.
- Evaluate the security measures in place for each touchpoint.
Implement Encryption
Encrypting data ensures it remains unreadable if intercepted:
- Use SSL/TLS for data in transit.
- Employ advanced encryption standards (AES) for data at rest.
- Implement secure key management practices.
Establish Strong Access Controls
Limit who can access PII:
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to assign permissions based on job roles.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
- Regularly review access privileges to ensure they align with business needs.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Stay ahead of vulnerabilities:
- Schedule regular updates for all software and systems.
- Conduct periodic security audits and penetration testing.
- Implement a patch management process.
Train Staff
Ensure your team understands the importance of PII protection:
- Conduct regular training sessions on data security best practices.
- Provide resources and support for ongoing education.
- Implement policies and procedures for handling PII.
Incident Response Plan
Be prepared for potential breaches:
- Develop a detailed incident response plan.
- Conduct drills to ensure your team is ready to act swiftly.
- Establish communication protocols for notifying customers and stakeholders.
Tools and Technologies for PII Protection

Several tools and technologies can aid in PII protection:
Encryption Software
Encryption software plays a crucial role in protecting personally identifiable information (PII). By transforming sensitive data into unreadable formats, these tools ensure that even if data is intercepted, it remains inaccessible without the proper decryption keys. Various encryption solutions are available, including file-level encryption, full disk encryption, and database encryption, each catering to different needs and storage solutions. When selecting encryption software, organizations should consider factors such as compliance with industry standards, ease of use, and integration capabilities with existing systems. Regularly updating encryption algorithms and practices is also essential to combat evolving security threats.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions are designed to monitor and control the flow of sensitive information across networks and endpoints. These systems help prevent unauthorized access, sharing, or transmission of PII by establishing rules and protocols. DLP technologies can flag or isolate sensitive data in real-time, providing alerts for potential breaches while allowing organizations to maintain strict control over their data. A robust DLP strategy complements existing security measures by adding another layer of protection against accidental data leaks or malicious insider threats.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Tools
Implementing Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools is critical for managing user access to sensitive data. IAM solutions enable organizations to enforce policies like user authentication, role-based access controls, and activity monitoring, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access PII. These tools often integrate with other systems to provide a comprehensive view of user activities, helping identify potential security risks or anomalies. By effectively managing identities and access privileges, organizations bolster their overall security posture and reduce the likelihood of unauthorized data access or breaches.
Regular Security Training and Awareness Programs
To create a secure environment for handling PII, regular security training and awareness programs are essential. These initiatives educate employees about the importance of data protection and make them aware of potential threats, such as phishing attacks or social engineering tactics. By fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations empower their staff to act as the first line of defense against data breaches. Continuous education, combined with practical simulations and real-world examples, helps cultivate vigilant and informed employees, further strengthening an organization’s PII protection strategy.
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, the protection of personally identifiable information (PII) has never been more critical. Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to data security, implementing a comprehensive framework that encompasses technical measures, employee training, and incident preparedness. By conducting thorough audits, employing robust encryption technologies, establishing stringent access controls, and ensuring ongoing staff education, businesses can significantly mitigate the risks associated with data breaches. Furthermore, incorporating tools like Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Identity and Access Management (IAM) can enhance security measures, creating a multi-layered defense against unauthorized access and data exposure. Ultimately, fostering a culture of security awareness and preparedness not only protects valuable customer information but also preserves trust and reputational integrity in an increasingly interconnected world.